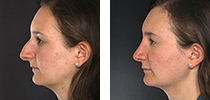
Macrotia
Conveniently located to serve the areas of New York, NY
Contents
Otoplasty for Large Ears
Otoplasty is a cosmetic plastic surgery procedure that corrects malformations of the outermost, visible part of the ear, the auricle. One such malformation is macrotia, or large ears. Macrotia occurs when the height of the ear exceeds the normal confines of the eyebrow, and the alar rim (the skin that runs alongside the nose, down to the nostril). It is similar to another condition of the outer ear known as prominent ears, or ears that stick out more than 2 cm (0.8 inch) from the side of the head. Macrotia differs from prominent ears in that the anatomical focus here is on size, not protrusion. Additionally, macrotia is less frequent than prominent ears, although the two may occur together.
aesthetic accompaniments to complete our face. In the same way that our eyes, nose, lips and facial structures are all unique, so, too are the size and shape of our ears. According to literature, the vertical height of the ear should be approximately six centimeters. (1) It can be both disheartening and upsetting if the face we see in the mirror is not how we want it to be. Moreover, if our ears are larger than average, it can make our facial proportions look unbalanced, and may even lead to unkind comments from others. Although we may wear our hair longer to help disguise them, we know they are still underneath.
With over forty years of plastic surgery experience, Dr. John E. Sherman, MD, FACS provides the highest quality otoplasty procedures in the heart of Manhattan. If you would like to alter the size of your ears with a safe, permanent surgery, please call our offices at your convenience at (212) 535-2300, or fill out our convenient inquiry form to get started with your request.
The Outer Ear
The function of the ear is to convert physical vibration into an encoded nervous impulse in the brain. (1) The flexible elastic cartilage, also known as the pinna, is the only visible structure of the ear. It comprises four main areas.
Tragus – The tragus is a small nodule-like protuberance of cartilage on the side of the head. It covers the ear canal slightly, and is responsible for directing sound toward the eardrum.
Helix – The helix is the prominent upper rim of the outer ear. The helical rim curls somewhat around the curvature of the auricle to help channel sounds into the ear canal.
Antihelix – The antihelix sits parallel to the helix on the pinna. It is a raised, thicker ridge of cartilage that curves forward, connecting with the other upper parts of the auricle.
Lobule – A familiar area for piercing, the lobule is the fleshy lower part of the auricle. Although they are not known to have any major biological function, it is thought earlobes may play a role in ear temperature regulation and balance.
Ear Proportions
With a shape well-suited to channeling sound, the auricle functions as an amplifier for complex sound waves as they travel into the ear canal. The auricle is angled to catch sounds from the front more than behind. This is helpful to localize sound and pinpoint its location. However, there are certain expectations when it comes to the anatomical appearance of our ears. For example, we would expect most adult ears to be well-proportioned compared to the rest of the face. Sometimes, especially with adolescents, both large and prominent ears may be more common and as-yet uncorrected. When unexpectedly large size occurs in the ears at any age, it can cause self-consciousness and body-esteem issues.
For comprehensive medical advice sensitive to your needs and top-tier plastic surgery in Manhattan, you can rely on Dr. Sherman. Conveniently located a stone’s throw from Central Park, Dr. Sherman’s offices are a comfortable, accommodating setting to aid you in achieving your aesthetic goals. Fill out an inquiry form on our website, or call us directly at (212) 535-2300 for more information about otoplasty procedures offered by Dr. Sherman.
Benefits of an Otoplasty Procedure
Facial disfigurement such as abnormal ear size can cause psychological distress, low self-esteem, and varying levels of social isolation. (3) However, an otoplasty may be the answer you are looking for. There are numerous benefits of an otoplasty procedure for patients who have been diagnosed with macrotia.
- Restores aesthetic balance
- Reduces ear profile
- Natural facial appearance
- Increased self-confidence
- Permanent results
- Safe cosmetic procedure
It is important for you to work with Dr. Sherman and be candid about your feelings about your ears and how their appearance has affected you personally. To get to know Dr. Sherman, and to find out more about his surgical philosophy, please watch his introductory video on YouTube!
Candidates for an Otoplasty Procedure
Candidates for an otoplasty procedure to reduce the size of their ears should be willing to take permanent surgical measures to achieve their cosmetic aesthetic goals. Generally speaking, good candidates for this type of treatment are adults who are dissatisfied with the size of their ears, and who have experienced significant psychological, social, and emotional impact from having large ears. If you are a resident of New York or a patient from out of town considering an otoplasty, please contact us to schedule a personal consultation with Dr. Sherman.
Personal Consultation
At your personal consultation with Dr. Sherman, you will have the opportunity to be open and honest about the difficulties you have faced because of your larger ears. Dr. Sherman treats hundreds of patients with similar circumstances every year and will treat your concerns with professionalism and sensitivity. During your one-on-one meeting, he will take a brief patient history and examine the dimensions of your ears both visibly and physically. He will assess your macrotia using standard otological measurements and, if he deems it necessary, will advise you on the next stage of your otoplasty. If you smoke, you will be advised to stop smoking six weeks before your otoplasty procedure, as the chemicals in cigarettes can adversely affect the healing process.
Find out more about a selection of plastic surgery procedures tailored to help you look your best by reading Dr. Sherman’s blog!
Otoplasty Procedure
Anesthesia
In adults, Dr. Sherman performs otoplasty procedures in the office ambulatory surgery center. Most of our ear reductions are performed under local anesthesia, although they may be performed with the addition of sedation anesthesia by a board-certified anesthesiologist by prior patient request.
What Happens During an Otoplasty Procedure?
During an otoplasty to reduce ear size, it is essential to address the area of excess, either the upper portion of the ear, the lower portion of the ear, or both areas. An anterior (frontal) incision is made, which may be combined with the posterior incision. These incisions are well concealed by the natural shape of the ear. Dr. Sherman then carefully manipulates the cartilage. When reducing the size of the helix, he removes a sliver-like portion along the helical rim of the ear. This readjusts the auricle to an aesthetically pleasing size and shape. This smaller and natural-looking appearance is achieved with the use of specialized tools. Once the cartilage has been removed and the tissues have been successfully aligned, Dr. Sherman carefully sutures the ear. On average, it takes between 2-3 hours to complete this procedure (both ears), depending on whether other aesthetic concerns such as prominent ears are addressed.
Recovery & Results of Ear Reduction Surgery
After your surgery, we will send you home in a hairdressing that we usually remove after 5-7
days. You may use doctor-approved over-the-counter pain relief and ice packs if you are experiencing discomfort. During the postoperative period, it is very important you treat your ears gently and avoid any vigorous activity that could involve inadvertently banging your head against anything. Dr. Sherman advises his otoplasty patients to use caution while sleeping, and avoid sleeping on their side entirely during the healing process. Additionally, you may do the following:
- Choose your clothing carefully so it does not catch.
- Avoid smoking/nicotine containing products.
- Sleep with your head elevated.
- Follow Dr. Sherman’s post-surgery instructions.
We will remove your sutures roughly ten days after your surgery. You will immediately notice the reduction in your ears’ size once the dressing is removed. However, the anatomical appearance of your ears will improve over the ensuing two months when the swelling goes down.
Stay in touch with Dr. Sherman and his team on social media. Like and follow us on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and YouTube!
Cost of Ear Size Reduction Surgery in Manhattan, NY
The cost of your otoplasty will depend on your individual circumstances. If you are combining treatments for both macrotia and prominent ears, your procedure will be longer. Please visit our website for financing options offered by Dr. Sherman.
FAQ
What is the medical name for big ears?
The medical name for ears that extend past normal parameters is macrotia. For ears that protrude outward further than average, the term “prominent ears” is used.
Is there a cosmetic surgery procedure for fixing ears?
Yes! Otoplasty is a plastic surgery procedure that can be performed by a board-certified plastic surgeon to adjust the size, prominence, or shape of the ears.
I feel self-conscious about my big ears, what can I do?
There are both surgical and non-surgical ways to help reduce self-consciousness about large ears. You may choose to cover them with clothing, or choose a haircut that makes them less conspicuous. As a more permanent solution, you may consider otoplasty, a plastic surgery procedure that can reduce the size of your ears by removing cartilage from the outer structure. Otoplasty surgery is popular with people with large or prominent ears because of natural, lifelong results.
References
- Kennedy, K. L., & Katrib, Z. (2021). Otoplasty. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538320/
- Alberti, P. (n.d.). 2 THE ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE EAR AND HEARING. https://www.who.int/occupational_health/publications/noise2.pdf
- Jones, E. S., Gibson, J. A. G., Dobbs, T. D., & Whitaker, I. S. (2020). The psychological, social and educational impact of prominent ears: A systematic review. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, 73(12), 2111–2120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2020.05.075